Health insurance is an important way to help manage the cost of medical care. Although there are many types of health insurance available, it can be confusing to know which one is best for you or your family. In this article, you will learn about different types of health insurance and how they work. Understanding the basics can help you make better choices about your healthcare. Each type of plan offers unique benefits and coverage options. As you read, you will see how these plans differ and what they offer. With the right information, you can confidently choose the plan that fits your needs. Now, explore the various options available in health insurance to find what suits you best.
Understanding the Basics of Health Insurance Plans
Health insurance plans are designed to help people pay for medical expenses. These plans usually cover doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription drugs, and preventive care. Additionally, health insurance often includes annual check-ups and screenings, which can help catch health problems early. By spreading the risk among many people, insurance companies can make healthcare more affordable. When you pay a monthly premium, you gain access to these services and financial protection.
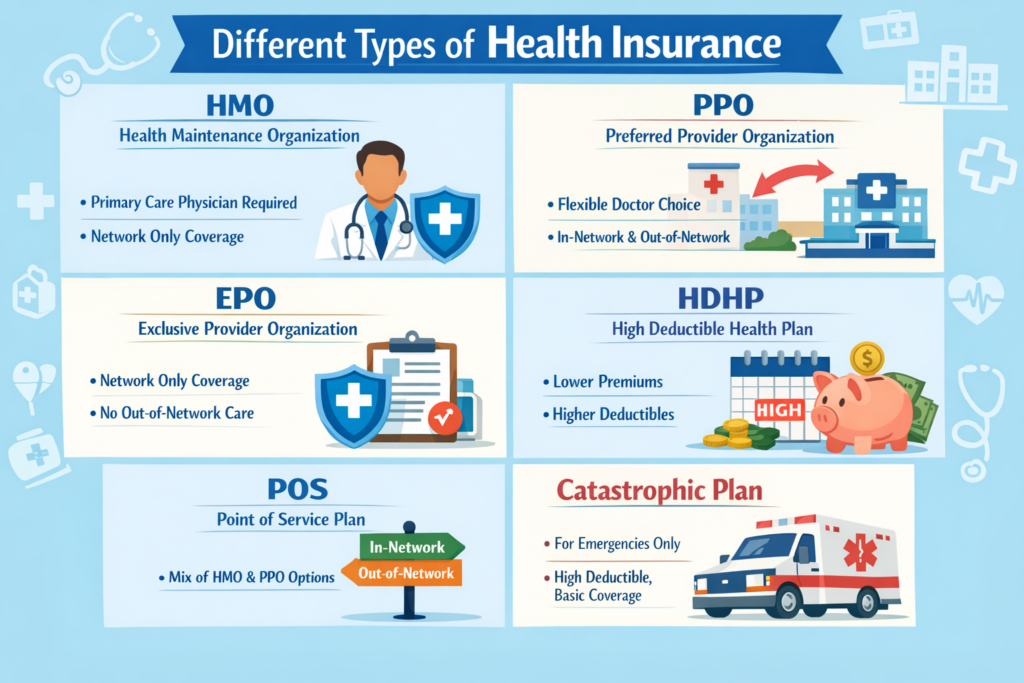
There are several types of basic health insurance plans, including Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs). Each type has its own network of doctors and hospitals, along with rules about referrals and coverage. For example, HMOs usually require you to choose a primary care doctor, while PPOs allow more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. EPOs limit coverage to a specific network but often do not require referrals. By understanding the differences, you can select a plan that works for your lifestyle.
Moreover, health insurance plans often have certain costs you must pay. These include deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance, which can vary by plan. The deductible is the amount you pay before the insurance starts to cover expenses. After you meet your deductible, most plans require copayments for visits and coinsurance for some services. Knowing about these costs helps you budget and plan for medical needs throughout the year.
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance Options Explained
Many people get health insurance through their employer, which often makes coverage more affordable. Employers usually pay a portion of the monthly premium, making it less expensive for employees. In addition, many employer-sponsored plans offer comprehensive coverage, including medical, dental, and vision care. By joining a group plan, you may also receive better benefits than you would on your own. Most companies work with insurance providers to offer a range of plan options.
Employers typically give employees a choice between different types of plans, such as HMOs, PPOs, or high-deductible health plans. Each option comes with its own set of costs and coverage levels. For example, a high-deductible plan may have lower monthly premiums but higher out-of-pocket expenses. Some employers also offer health savings accounts, which allow you to save money tax-free for medical expenses. Employees can choose the plan that best fits their health needs and budget.
Enrollment in employer-sponsored health insurance usually occurs once a year during an open enrollment period. During this time, you can select a new plan, add dependents, or make changes to your coverage. Outside of open enrollment, you can only make changes if you experience a qualifying life event, such as marriage or the birth of a child. Employees should review their options carefully before making a decision. By understanding what is available, you can get the most value from your employer’s health insurance offerings.
Exploring Government Health Insurance Programs
Government health insurance programs help millions of people access affordable healthcare. Two of the most well-known programs are Medicaid and Medicare. Medicaid provides coverage for low-income individuals and families, while Medicare serves people age 65 and older, as well as those with certain disabilities. Each program operates differently and follows its own eligibility rules. These programs fill important gaps in the health insurance market.
Medicaid is funded jointly by the federal and state governments and is managed at the state level. Eligibility and benefits can vary from one state to another. Medicaid typically covers a wide range of services, including doctor visits, hospital care, and long-term care. Some states have expanded Medicaid to cover more people under the Affordable Care Act. Medicaid can be a vital resource for those who may not qualify for other types of health insurance.
Medicare is a national program with several parts. Part A covers hospital stays, Part B covers medical services, and Part D covers prescription drugs. Some people also choose Medicare Advantage plans, which are private plans that provide additional benefits. People who qualify for Medicare pay monthly premiums, but some costs are covered by the government. Understanding the details of each part helps beneficiaries get the most out of their coverage.
Individual and Family Health Insurance Policies
When employer coverage is not available, many people turn to individual and family health insurance policies. These plans can be purchased directly from insurance companies or through state and federal marketplaces. You can compare different plans to find the coverage and price that meet your needs. Often, families choose these policies to ensure that everyone in the household has essential healthcare protection. The flexibility of these plans makes them a popular option.
Individual and family health plans must meet the requirements set by the Affordable Care Act. This means they must cover essential health benefits, such as emergency services, maternity care, and mental health treatment. Insurance companies cannot deny coverage based on pre-existing conditions. By shopping around, you can find plans with lower premiums, but you might face higher out-of-pocket costs. Evaluating your health needs is important before choosing a policy.
Enrollment in individual and family health insurance usually happens during an annual open enrollment period. Special enrollment periods are available for people who experience life changes, like losing other coverage or moving to a new state. Applying through the marketplace can also make you eligible for subsidies to lower your monthly premium. Careful research and comparison can help you find a plan that fits your budget and healthcare needs. Individual and family policies offer both flexibility and important protection for those without access to group insurance.
Comparing Supplemental and Specialty Insurance Plans
While basic health insurance covers many needs, some people choose supplemental or specialty insurance for extra protection. Supplemental insurance plans can help cover costs that your main insurance does not pay. For example, you might purchase a plan for dental care, vision care, or prescription drugs. These plans can reduce your out-of-pocket expenses and provide peace of mind. Some people also buy supplemental coverage for accidents, critical illness, or hospital stays.
Specialty insurance plans focus on specific health needs or risks. For instance, travel health insurance covers medical emergencies when you are traveling abroad. Long-term care insurance helps pay for extended care not covered by regular health insurance, such as nursing home stays. Cancer and disease-specific policies offer financial support if you are diagnosed with certain illnesses. By adding specialty coverage, you can tailor your insurance to your unique situation.
Choosing supplemental or specialty plans usually involves paying an extra premium each month. However, the added coverage can be worth the cost if you have specific health concerns or want extra financial protection. Always read the plan details to understand what is covered and any limitations. Comparing different policies can help you find the right balance between cost and coverage. Supplemental and specialty plans can be a smart addition to your health insurance strategy.
Conclusion
As you have seen, there are many different types of health insurance to fit a variety of needs and situations. Understanding the basics of health insurance plans can help you sort through the many options available. Employer-sponsored health insurance often provides comprehensive benefits at a lower cost, while government programs offer vital support to those who qualify. If you do not have access to group insurance, individual and family policies can give you flexible and essential coverage. Supplemental and specialty plans can help fill the gaps, offering extra peace of mind for unexpected costs.
